The State of Ireland's Mobile Networks: Summer 2019
An in-depth analysis of Ireland's mobile networks as we teeter on the cusp of another wireless generation.
Published 02/07/19
If ever there was a time to be excited about the prospect of a gigabit society on the Emerald Isle, we’re racing towards it. The stars are lining up for the next generation of wireless to connect not just everyone, but everything. For you and I, that’s a bewitching trajectory, and one which is destined to etch its way into history.
But, the future is about more than just 5G, contrary to what the manufactured geopolitical storm surrounding it would have us think. And, on that note of fabrication, it’s high time that we banish the ridiculous concept of 5G, alone, enabling avant-grade applications such as remote surgeries and holographic calling.
In fact, it is the endless array of technologies that 5G will contribute to, from the decentralisation of compute resources with edge computing to the proliferation of augmented reality, blockchain and beyond, which should intrigue us most profoundly. We, and by that extension, Ireland, is teetering on the edge of converging technological revolutions.
It is not often that Ireland’s stereotypically drab telecoms industry is awash with ambition and enthusiasm for its future, but this time things are different. So, let’s run with that premise and criss-cross the developments changing the face of connectivity on our island.
(Note: Make yourself comfortable. This is an unapologetically in-depth article.)
But, the future is about more than just 5G, contrary to what the manufactured geopolitical storm surrounding it would have us think. And, on that note of fabrication, it’s high time that we banish the ridiculous concept of 5G, alone, enabling avant-grade applications such as remote surgeries and holographic calling.
In fact, it is the endless array of technologies that 5G will contribute to, from the decentralisation of compute resources with edge computing to the proliferation of augmented reality, blockchain and beyond, which should intrigue us most profoundly. We, and by that extension, Ireland, is teetering on the edge of converging technological revolutions.
It is not often that Ireland’s stereotypically drab telecoms industry is awash with ambition and enthusiasm for its future, but this time things are different. So, let’s run with that premise and criss-cross the developments changing the face of connectivity on our island.
(Note: Make yourself comfortable. This is an unapologetically in-depth article.)
With the 4G cycle drawing to a close, are there any winners?
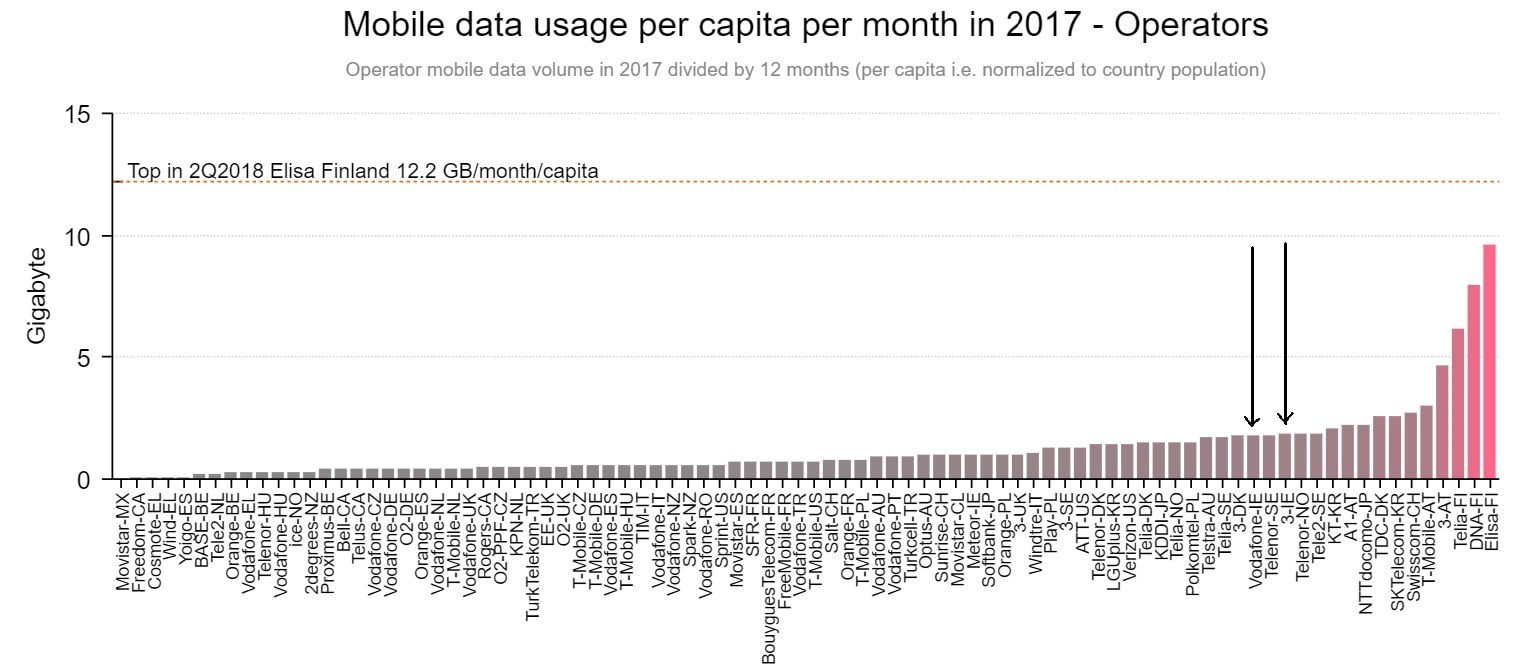
The deployment of pervasive 4G networks on the island of Ireland has been a colourful, if at times, frustrating, endeavour to watch. Not only did we feel the far-reaching impacts of market contraction with the consolidation of Three and Telefonica’s O2, but we also witnessed Ireland go from being one of the most expensive places in the world for mobile data to being one of the cheapest, all within a very short space of time.
In particular, while Three’s merger with O2 in 2015 has not radically changed the distribution of revenues in the mobile market, it has invigorated competition on the fronts of pricing and network quality. The latter aspect is perhaps the most significant one because it highlights the fact that a dramatic shift in fortunes is abound.
While scoffed at in its primitive state, including by myself, Three’s mobile network is now a far cry from the dysfunctional, crippled version of yesteryear. Today, its 4G network offers more capacity than that of both Vodafone and eir in most locations, benefitting directly from three-carrier aggregation and higher modulations (256 QAM).
By gravitating towards a site grid which is composed of many multi-band macrosites, Three has stormed ahead of its competitors for sheer throughput with 4G, blazing past the 400Mbps mark. This kind of network performance has been achieved with thanks to Three’s enviable spectrum portfolio, which expanded considerably as a result of the merger.
In particular, while Three’s merger with O2 in 2015 has not radically changed the distribution of revenues in the mobile market, it has invigorated competition on the fronts of pricing and network quality. The latter aspect is perhaps the most significant one because it highlights the fact that a dramatic shift in fortunes is abound.
While scoffed at in its primitive state, including by myself, Three’s mobile network is now a far cry from the dysfunctional, crippled version of yesteryear. Today, its 4G network offers more capacity than that of both Vodafone and eir in most locations, benefitting directly from three-carrier aggregation and higher modulations (256 QAM).
By gravitating towards a site grid which is composed of many multi-band macrosites, Three has stormed ahead of its competitors for sheer throughput with 4G, blazing past the 400Mbps mark. This kind of network performance has been achieved with thanks to Three’s enviable spectrum portfolio, which expanded considerably as a result of the merger.
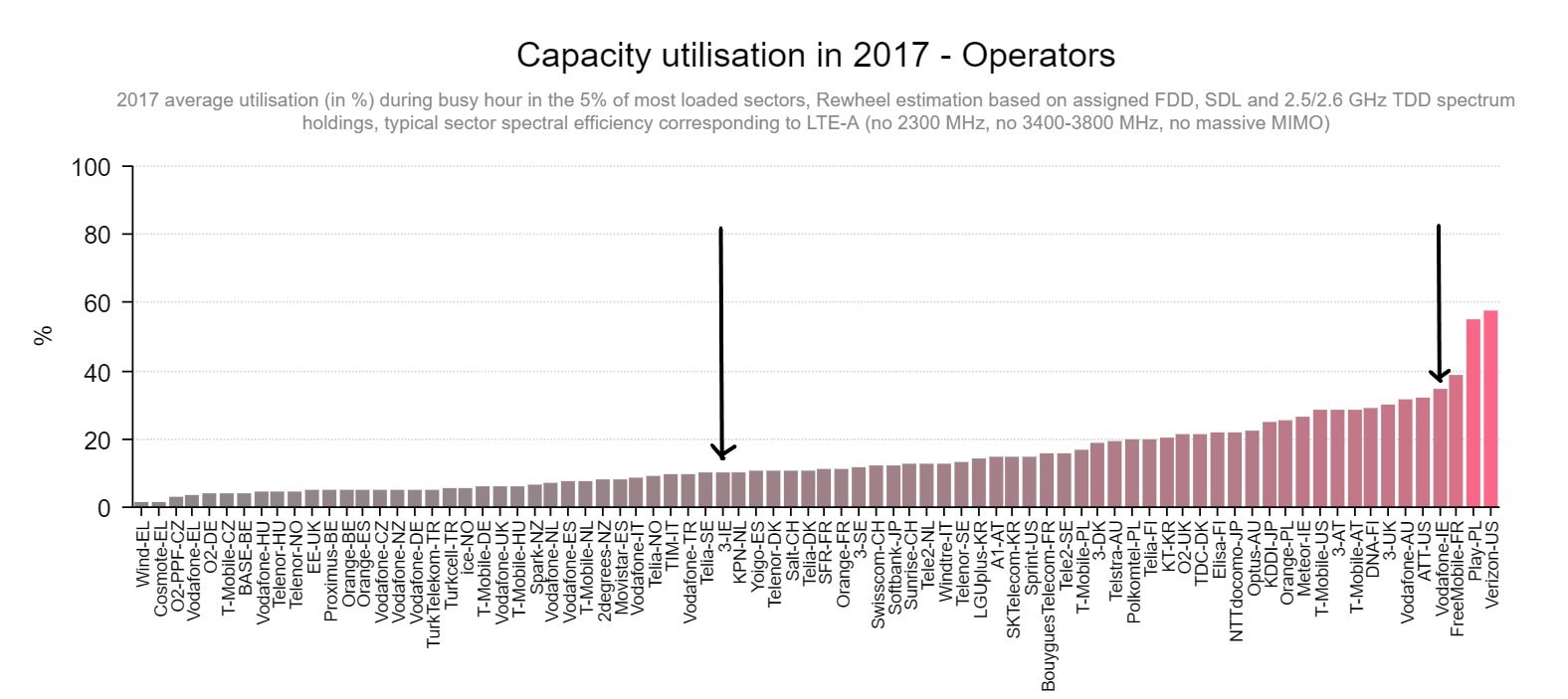
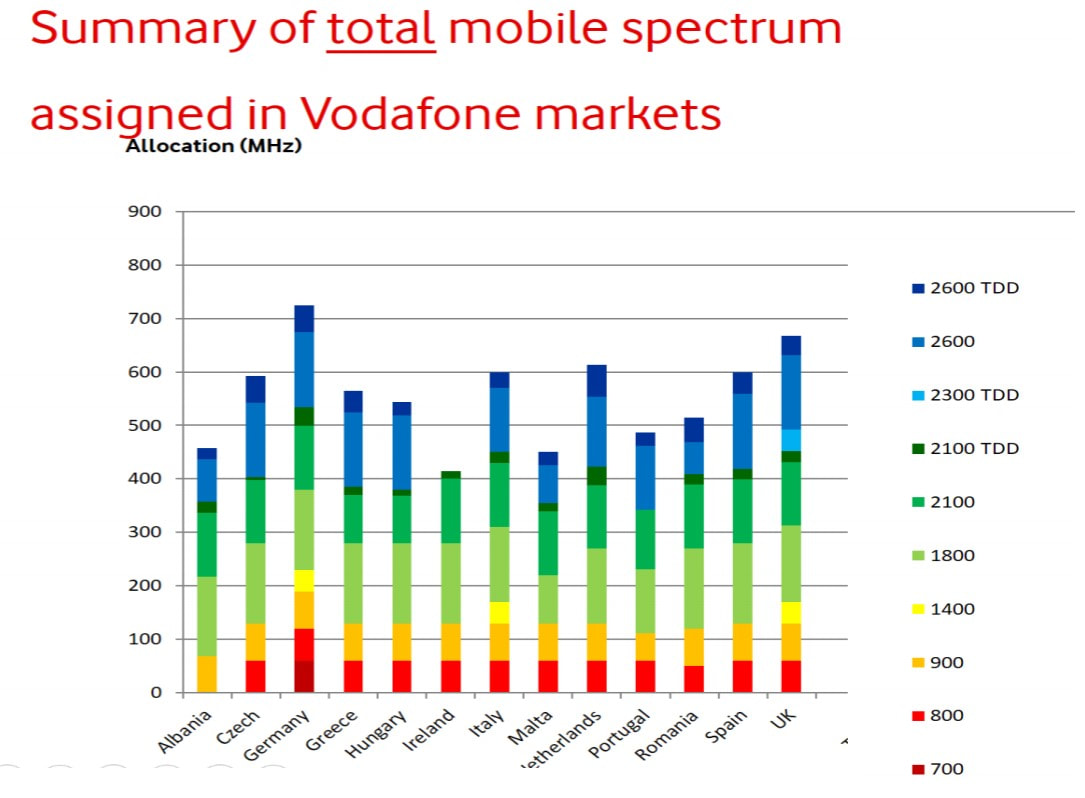
For an insight into the stark capacity divide that has developed between Ireland’s mobile operators, we should examine the make-up of their networks in urban and suburban areas, where the peak traffic load is greatest. Three is providing 45MHz of capacity, composed of three carriers as follows - 1800MHz (20MHz), 1800MHz (15MHz), 800MHz (10MHz).
To the dismay of Vodafone and eir, who have been left disadvantaged as a result of the merger, they are seriously restricted by their spectrum assets. Vodafone is offering 30MHz of capacity - 1800MHz (20MHz), 800MHz (10MHz) - where Three is able to provide 45MHz. That’s a 50% difference between the two operators.
And the divide is even more evident with eir’s 4G network, with just 25MHz of capacity at disposal - 1800MHz (15MHz), 800MHz (10MHz). Even with densification of the site grid, Vodafone and eir will remain behind Three in terms of network capacity, and this will only be exacerbated by data traffic growth.
To the dismay of Vodafone and eir, who have been left disadvantaged as a result of the merger, they are seriously restricted by their spectrum assets. Vodafone is offering 30MHz of capacity - 1800MHz (20MHz), 800MHz (10MHz) - where Three is able to provide 45MHz. That’s a 50% difference between the two operators.
And the divide is even more evident with eir’s 4G network, with just 25MHz of capacity at disposal - 1800MHz (15MHz), 800MHz (10MHz). Even with densification of the site grid, Vodafone and eir will remain behind Three in terms of network capacity, and this will only be exacerbated by data traffic growth.
However, despite the above, all is not as it seems. Three’s network facilitates a disproportionate volume of data traffic relative to its subscriber count, a result that can be attributed to its all-in approach to unlimited data allowances. In effect, this means that Three, by very nature, has to offer more capacity than its competitors if it is to provide comparable network performance.
To understand the very material impact of congestion on mobile networks, we should compare each operator in the densest conditions, think central business districts and train stations during rush hour. Here, even with the least capacity, eir’s network tops the download speed charts, at least in my experience.
Vodafone comes in a close second, trailed somewhat by Three. That gives Big Red and eir some breathing ground, for now. However, the gap is narrowing. Congestion is becoming a more prevalent issue with both Vodafone and eir’s network, prompting average download speeds to slide and latency to increase.
To understand the very material impact of congestion on mobile networks, we should compare each operator in the densest conditions, think central business districts and train stations during rush hour. Here, even with the least capacity, eir’s network tops the download speed charts, at least in my experience.
Vodafone comes in a close second, trailed somewhat by Three. That gives Big Red and eir some breathing ground, for now. However, the gap is narrowing. Congestion is becoming a more prevalent issue with both Vodafone and eir’s network, prompting average download speeds to slide and latency to increase.
Just one quick glance at Vodafone’s portfolio of plans will explain the degradation in network performance. It is being forced, begrudgingly, to increase data allowances for both pay as you go and bill pay customers. A similar trend has infiltrated eir, in its case, leading to the zero-rating of data traffic generated by social media use.
Luckily, there are techniques, beyond aggregating more spectrum, that Ireland’s mobile operators can pursue to enhance network performance in dense urban environments. Densification with small cells, as mentioned already, is one of these. However, perhaps the most cost-effective manner to bring about performance gains is to boost spectral efficiency.
This can be achieved with 256 QAM and MIMO (both 4x4 and 8x8). The former technique is being exploited by Three and Vodafone, and eir has followed suit in recent times. However, the performance benefits of 256 QAM, for example, can only be realised when supported devices are in good signal conditions, effectively eradicating gains within much of a macosite’s coverage footprint.
It is the very real limitations of the above technologies that highlight the underlying criticality of a large and diverse spectrum portfolio. Three will wield an increasing capacity advantage over its competitors until more spectrum is released - an issue that I will discuss later in this article.
Luckily, there are techniques, beyond aggregating more spectrum, that Ireland’s mobile operators can pursue to enhance network performance in dense urban environments. Densification with small cells, as mentioned already, is one of these. However, perhaps the most cost-effective manner to bring about performance gains is to boost spectral efficiency.
This can be achieved with 256 QAM and MIMO (both 4x4 and 8x8). The former technique is being exploited by Three and Vodafone, and eir has followed suit in recent times. However, the performance benefits of 256 QAM, for example, can only be realised when supported devices are in good signal conditions, effectively eradicating gains within much of a macosite’s coverage footprint.
It is the very real limitations of the above technologies that highlight the underlying criticality of a large and diverse spectrum portfolio. Three will wield an increasing capacity advantage over its competitors until more spectrum is released - an issue that I will discuss later in this article.
In a country where broadband is a luxury, 4G coverage defines network performance.
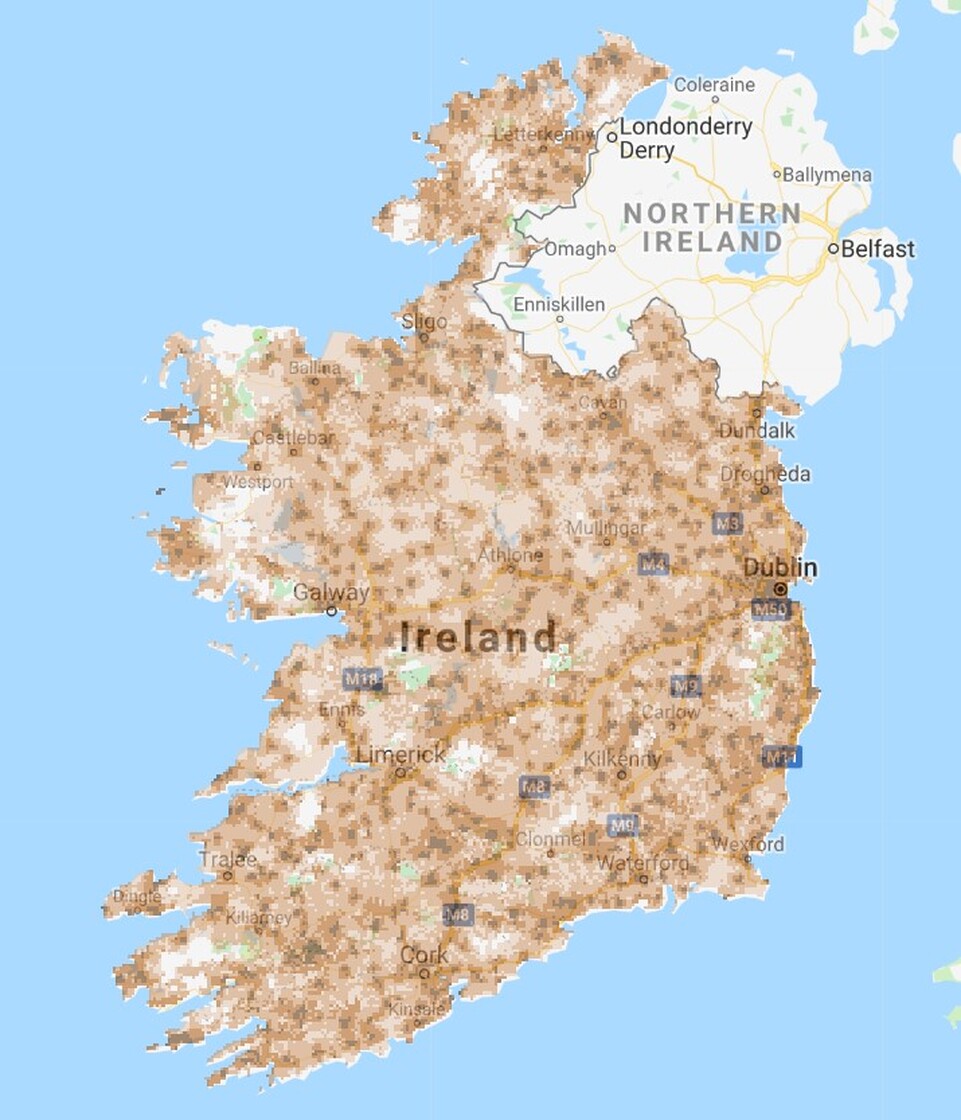
Capacity is just one angle of network performance, however, and coverage availability is equally as important, particularly in a country where there is an abhorrent digital divide. On this front, Vodafone continues to reign supreme, with its 4G network blanketing more of Ireland’s physical landmass than any other.
Big Red’s low-band 4G network (10MHz of 800MHz) transcends urban Ireland and touches rural towns, villages and lands to a more pervasive degree than the networks of both Three and eir. This coverage advantage, while declining, allows Vodafone to continue charging a lamentable premium for its services.
Meanwhile, eir lags Vodafone and Three for 4G coverage in rural areas, and the number of macrosites onto which it has deployed carrier aggregation is limited to an alarming degree. Adding insult to injury, its 4G network stands on a very weak 3G foundation. Who mentioned a statue?
Thankfully, eir has openly acknowledged the very palpable shortcomings of its network and committed to extending 4G coverage to 99% of Ireland’s population, which will lead to a significant incidental increase in geographic coverage as a result.
But, one should question the authenticity of eir’s network proposals, especially as it trots out claims that are simply not true. For example, the operator and some of its leading executives have gone on record to explicitly state that eir will provide the most extensive 4G coverage in the world on completion of its upgrade programme, something that is just inconceivable.
Big Red’s low-band 4G network (10MHz of 800MHz) transcends urban Ireland and touches rural towns, villages and lands to a more pervasive degree than the networks of both Three and eir. This coverage advantage, while declining, allows Vodafone to continue charging a lamentable premium for its services.
Meanwhile, eir lags Vodafone and Three for 4G coverage in rural areas, and the number of macrosites onto which it has deployed carrier aggregation is limited to an alarming degree. Adding insult to injury, its 4G network stands on a very weak 3G foundation. Who mentioned a statue?
Thankfully, eir has openly acknowledged the very palpable shortcomings of its network and committed to extending 4G coverage to 99% of Ireland’s population, which will lead to a significant incidental increase in geographic coverage as a result.
But, one should question the authenticity of eir’s network proposals, especially as it trots out claims that are simply not true. For example, the operator and some of its leading executives have gone on record to explicitly state that eir will provide the most extensive 4G coverage in the world on completion of its upgrade programme, something that is just inconceivable.
Cignal is the company behind the expansion of 4G into rural Ireland, providing its infrastructure to operators such as eir and Imagine. Born out of an acquisition of three-hundred radio sites from semi-state company Coilte in 2015, Cignal has lodged planning permission for a large number of new radio sites in recent times.
This expansion of rural infrastructure by Cignal coincides with a wider industry effort to reduce the number and size of connectivity blackspots in Ireland, an issue that compelled the government to establish the Mobile Phone and Broadband Taskforce. And to its credit, eir has made a profound contribution to this effort by pioneering WiFi Calling.
According to figures sighted by the Mobile Phone and Broadband Taskforce, adoption of WiFi Calling on eir’s network has been strong, an indication that customers are actively seeking to enhance their calling experience. This feature has performed admirably in my testing, even on DSL-based fixed networks with download speeds struggling to exceed 3Mbps.
Vodafone is following in eir’s footsteps by beginning to support WiFi Calling on its network. However, Big Red’s implementation is rife with issues, lacking support while roaming abroad and producing issues with call diverts to voicemail. It is also repugnant that the operator has chosen to limit WiFi Calling to a select array of bill pay plans.
This expansion of rural infrastructure by Cignal coincides with a wider industry effort to reduce the number and size of connectivity blackspots in Ireland, an issue that compelled the government to establish the Mobile Phone and Broadband Taskforce. And to its credit, eir has made a profound contribution to this effort by pioneering WiFi Calling.
According to figures sighted by the Mobile Phone and Broadband Taskforce, adoption of WiFi Calling on eir’s network has been strong, an indication that customers are actively seeking to enhance their calling experience. This feature has performed admirably in my testing, even on DSL-based fixed networks with download speeds struggling to exceed 3Mbps.
Vodafone is following in eir’s footsteps by beginning to support WiFi Calling on its network. However, Big Red’s implementation is rife with issues, lacking support while roaming abroad and producing issues with call diverts to voicemail. It is also repugnant that the operator has chosen to limit WiFi Calling to a select array of bill pay plans.
Unfortunately, Three has thus far snubbed WiFi Calling, hardly a surprise given the fact that its brand is less dependent on a perception of network quality than that of Vodafone. Apathy for such a transformational feature won’t cut the mustard for much longer, however, and Three should be careful not to repeat the mistakes that defined its former self.
In terms of VoLTE, it is embarrassing that Ireland’s operators are still dependent on a circuit-switched fallback (CSFB) architecture in 2019. While each operator has announced plans to enable VoLTE on their networks, nothing has materialised as of yet.
Vodafone claims to have activated the feature on its network, but ironically, I’ve never been able to take advantage of it in my testing across numerous different smartphones and plans. Something's not quite right there.
(For a more thorough examination of the technologies that underpin WiFi Calling and VoLTE, refer to my article here.)
In terms of VoLTE, it is embarrassing that Ireland’s operators are still dependent on a circuit-switched fallback (CSFB) architecture in 2019. While each operator has announced plans to enable VoLTE on their networks, nothing has materialised as of yet.
Vodafone claims to have activated the feature on its network, but ironically, I’ve never been able to take advantage of it in my testing across numerous different smartphones and plans. Something's not quite right there.
(For a more thorough examination of the technologies that underpin WiFi Calling and VoLTE, refer to my article here.)
Peeling back the competitive implications of a stark spectrum disparity.
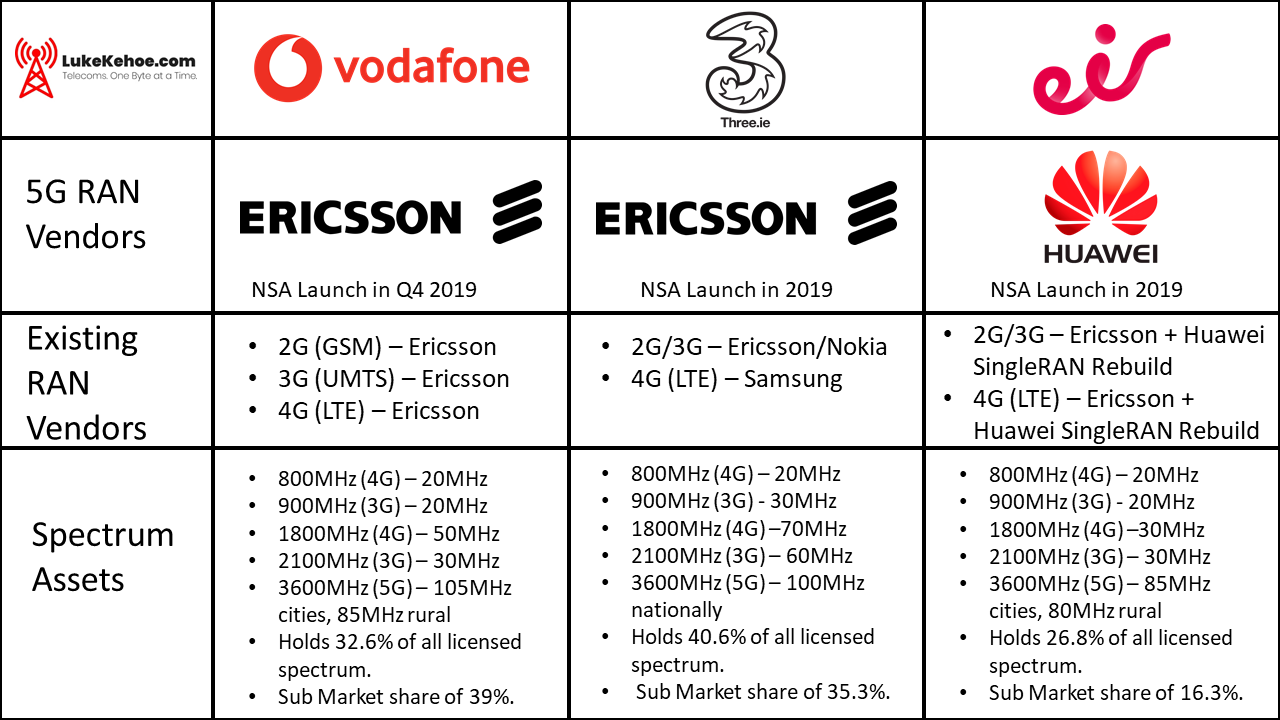
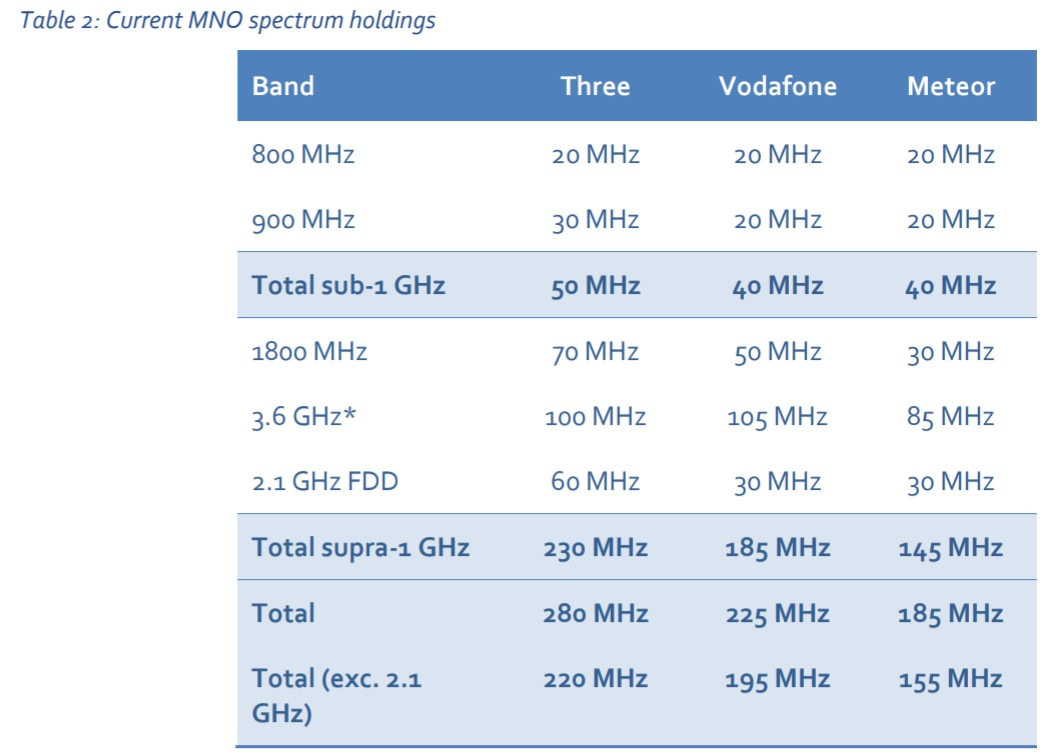
While there is a spectrum disparity in high-bands, the same is not true with the low-band assets of Ireland’s mobile operators. Here, there is a symmetrical allocation of 20MHz of capacity in the 800MHz band across each operator. This is a result of Three’s failure to acquire low-band spectrum in the 2012 multi-band award, leaving it with O2’s assets.
Three does hold an advantage in the 900MHz band, however, with 30MHz of capacity compared to the 20MHz held by Vodafone and eir, but this spectrum has been limited to 2G (GSM) and 3G (UMTS) services so far.
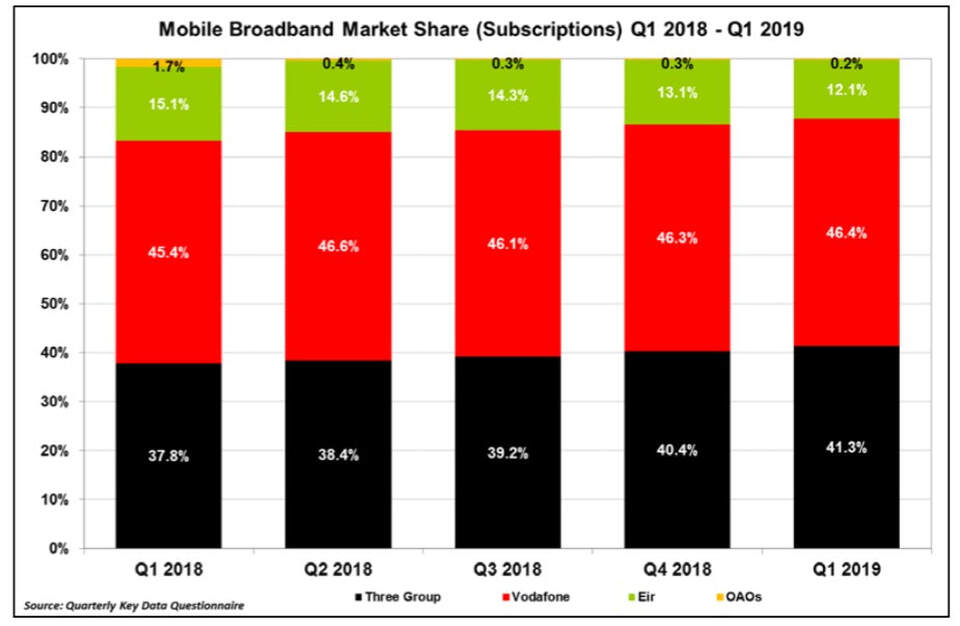
In light of the above, it is key to remember that the utilisation of 4G networks for mobile broadband is greatest in rural Ireland, and Vodafone and Three dominate this market with shares of 46.4% and 41.3% respectively - ComReg, Q1 2019.
Three does hold an advantage in the 900MHz band, however, with 30MHz of capacity compared to the 20MHz held by Vodafone and eir, but this spectrum has been limited to 2G (GSM) and 3G (UMTS) services so far.
In light of the above, it is key to remember that the utilisation of 4G networks for mobile broadband is greatest in rural Ireland, and Vodafone and Three dominate this market with shares of 46.4% and 41.3% respectively - ComReg, Q1 2019.
The trailing of eir for mobile broadband can be attributed to its poorer network and strategically limited data allowances, which are designed so as to prevent cannibalisation of revenues amassed from its fixed offerings.
The fact that mobile broadband subscriptions make up a disproportionate amount of data traffic compared to smartphone users, combined with the symmetrical low-band spectrum portfolio across operators, means eir’s 4G network is the least congested in rural Ireland, but only where there is a universal absence of carrier aggregation.
The fact that mobile broadband subscriptions make up a disproportionate amount of data traffic compared to smartphone users, combined with the symmetrical low-band spectrum portfolio across operators, means eir’s 4G network is the least congested in rural Ireland, but only where there is a universal absence of carrier aggregation.
What does the enlisting of Huawei mean for eir?
Behind the scenes, there has been a radical shift in the vendor choices of Ireland’s operators, something of critical importance as 5G commercialisation looms. I will refrain from dwelling on the “security” implications of such choices in this article, frankly because the geopolitical tirade against China is irrelevant in this context.
Speaking of China, its most prestigious telecoms vendor, Huawei, is now on track to provide equipment for the radio access network of eir, representing a remarkable ascension in the Irish market.
For Irish consumers, the enlisting of Huawei should be met with a cheer, particularly as the superiority of the vendor’s Massive MIMO (64T64R) offerings becomes more obvious. It’s the latter point that is often overlooked, Huawei is excellence exemplified for sub-6GHz 5G, offering a potent blend of cutting-edge performance and competitive pricing.
Eir has publicly proclaimed a partnership with Huawei for its radio access network, applying to both 4G (rebuild) and 5G. This is hardly surprising given the operator’s endorsement of Huawei for VDSL and GPON equipment. However, it does allude to a run away from Ericsson, which supported eir’s 2G, 3G and 4G networks.
Given the merger with O2, things are more complex at Three, exposing some of the skeletons in its closet. While the operator has not officially stated a vendor of choice for 5G quite yet, industry sources suggest Ericsson is being reeled in after attempts to adopt Huawei were met with a backlash from its business customers. This has not been an issue for eir given its smaller focus on enterprise customers.
For Irish consumers, the enlisting of Huawei should be met with a cheer, particularly as the superiority of the vendor’s Massive MIMO (64T64R) offerings becomes more obvious. It’s the latter point that is often overlooked, Huawei is excellence exemplified for sub-6GHz 5G, offering a potent blend of cutting-edge performance and competitive pricing.
Eir has publicly proclaimed a partnership with Huawei for its radio access network, applying to both 4G (rebuild) and 5G. This is hardly surprising given the operator’s endorsement of Huawei for VDSL and GPON equipment. However, it does allude to a run away from Ericsson, which supported eir’s 2G, 3G and 4G networks.
Given the merger with O2, things are more complex at Three, exposing some of the skeletons in its closet. While the operator has not officially stated a vendor of choice for 5G quite yet, industry sources suggest Ericsson is being reeled in after attempts to adopt Huawei were met with a backlash from its business customers. This has not been an issue for eir given its smaller focus on enterprise customers.
For Vodafone, things stand in stark contrast to its competitors, thanks to a perpetual relationship with Ericsson. Big Red’s radio access network is almost exclusively composed of equipment from the Swedish vendor, including remote radio units (such as RRUS11, RRUS12) and Active Integrated Radio (AIR) antennas.
The above means Vodafone’s network architecture is significantly less complex than that of Three and eir, providing benefits in the realm of cost efficiency. For mobility performance, especially when a customer transitions between the coverage footprint of radio sites, Vodafone’s network is vastly more consistent and reliable.
The above means Vodafone’s network architecture is significantly less complex than that of Three and eir, providing benefits in the realm of cost efficiency. For mobility performance, especially when a customer transitions between the coverage footprint of radio sites, Vodafone’s network is vastly more consistent and reliable.
The 3.6GHz auction is bringing neutral-host to Ireland.
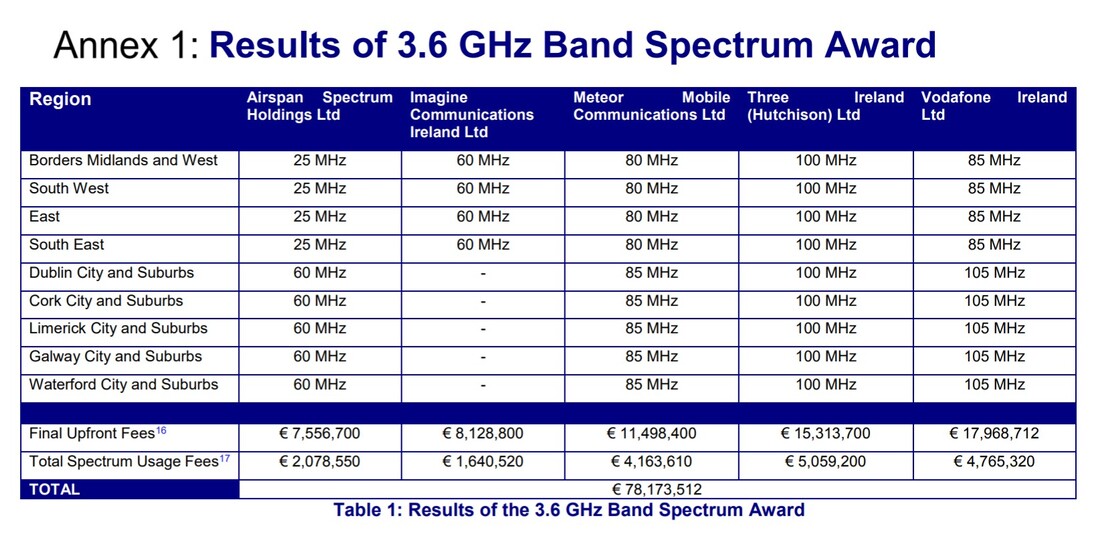
In 2017, to much applaud within Europe’s telecoms industry, ComReg awarded 350MHz of spectrum in the 3.6GHz band. This auction was very successful on a number of key points, allowing each of Ireland’s operators to gain access to a large contiguous (80-105MHz) allocation of sub-6GHz spectrum at a reasonable price.
Unlike similar auctions in countries such as Italy, ComReg’s allocation prevented distortion of costs by avoiding the creation of artificial scarcity, leading to an optimal market price of €0.04 per MHz of population. By contrast, in Italy, where Agcom released 200MHz of spectrum in the 3.6GHz band, there was an extraordinary market price of €0.29 per MHz of population.
The link between high spectrum prices and lower investment is being studied within the industry at the moment, but early conclusions yield an unsurprising finding - the embracement of policies which discourage high spectrum prices can help boost investment in telecoms infrastructure.
Outside of cost, the 3.6GHz auction was successful in ensuring both mobile operators and fixed wireless access (FWA) providers could compete and gain access to valuable mid-band spectrum. Ireland’s largest FWA provider, Imagine, secured 60MHz of spectrum within each rural region, supporting its aspirations to provide a wireless service capable of 150Mbps.
Unlike similar auctions in countries such as Italy, ComReg’s allocation prevented distortion of costs by avoiding the creation of artificial scarcity, leading to an optimal market price of €0.04 per MHz of population. By contrast, in Italy, where Agcom released 200MHz of spectrum in the 3.6GHz band, there was an extraordinary market price of €0.29 per MHz of population.
The link between high spectrum prices and lower investment is being studied within the industry at the moment, but early conclusions yield an unsurprising finding - the embracement of policies which discourage high spectrum prices can help boost investment in telecoms infrastructure.
Outside of cost, the 3.6GHz auction was successful in ensuring both mobile operators and fixed wireless access (FWA) providers could compete and gain access to valuable mid-band spectrum. Ireland’s largest FWA provider, Imagine, secured 60MHz of spectrum within each rural region, supporting its aspirations to provide a wireless service capable of 150Mbps.
As detailed earlier, the expansion of Imagine’s network will be mostly facilitated by Cignal, making enhanced connectivity available to a large proportion of premises within the amber intervention area of the National Broadband Plan. With a goal to deploy 325 sites, over 118 of which have already been deployed, Imagine is now reportedly examining the possibility of opening up its network to third-party retailers.
Beyond Ireland’s three operators and Imagine, Airspan’s Dense Air was the other winner of spectrum in the 3.6GHz band, gaining 25MHz in rural regions and 60MHz in cities. As a new entrant in the Irish market, Dense Air has been vocal about its intentions to amass further spectrum in high-bands, provided ComReg keeps prices at an appropriate level.
In my eyes, the emergence of Dense Air, and more specifically, the neutral-host model that it proposes, is an exciting development. For some context, Dense Air will utilise its licensed (and unlicensed) spectrum assets to deploy small cells, achieving a dense site grid, where there are underlying capacity and coverage shortcomings on the macrosite network today.
Beyond Ireland’s three operators and Imagine, Airspan’s Dense Air was the other winner of spectrum in the 3.6GHz band, gaining 25MHz in rural regions and 60MHz in cities. As a new entrant in the Irish market, Dense Air has been vocal about its intentions to amass further spectrum in high-bands, provided ComReg keeps prices at an appropriate level.
In my eyes, the emergence of Dense Air, and more specifically, the neutral-host model that it proposes, is an exciting development. For some context, Dense Air will utilise its licensed (and unlicensed) spectrum assets to deploy small cells, achieving a dense site grid, where there are underlying capacity and coverage shortcomings on the macrosite network today.
With a neutral-host model, Dense Air can become a wholesale provider of wireless coverage and capacity on-demand, allowing Irish operators to rent roaming access on its network. The small cells, for reference, will operate at low power to permit aggressive spectrum re-use, with the potential to exploit unlicensed and shared bands such as 6GHz in the future.
Mark my words, this concept of a neutral-host model for mobile networks is a game-changer, and the densification requirements introduced by gravitation towards higher frequencies with 5G will act as a catalyst for its adoption. It will be fascinating to watch the impact of Dense Air’s presence in the Irish mobile market moving forward.
Mark my words, this concept of a neutral-host model for mobile networks is a game-changer, and the densification requirements introduced by gravitation towards higher frequencies with 5G will act as a catalyst for its adoption. It will be fascinating to watch the impact of Dense Air’s presence in the Irish mobile market moving forward.
Trouble is in the air at 3.6GHz
Unfortunately, ComReg’s release of the 3.6GHz band has not been entirely free from trouble, and the failure to migrate incumbent users out of the spectrum is stalling the deployment of sub-6GHz 5G on this island. Such a precedent, in the continued absence of rectification, has major ramifications for Ireland’s mobile market, and sweeping things under the carpet won’t help.
To understand how this predicament materialised, we need to examine the 3.6GHz band in further detail. Prior to the awarding of liberalised use licenses in 2017, the spectrum was used to provide wireless broadband services, mostly in rural areas where there was no alternative connectivity solution available.
Wireless Internet Services Providers (WISPs) such as Ripplecom, Lightnet and even Imagine were the incumbent users of the 3.6GHz band at the time of its awarding, serving 21,665 customers according to ComReg.
To understand how this predicament materialised, we need to examine the 3.6GHz band in further detail. Prior to the awarding of liberalised use licenses in 2017, the spectrum was used to provide wireless broadband services, mostly in rural areas where there was no alternative connectivity solution available.
Wireless Internet Services Providers (WISPs) such as Ripplecom, Lightnet and even Imagine were the incumbent users of the 3.6GHz band at the time of its awarding, serving 21,665 customers according to ComReg.
In effect, this meant that Irish operators purchased brownfield spectrum in the 3.6GHz auction, with the knowledge that there was a potential for delayed access to lots within each region. To minimise the disruption of service for incumbent users, ComReg implemented a transition licensing framework across 292 services areas.
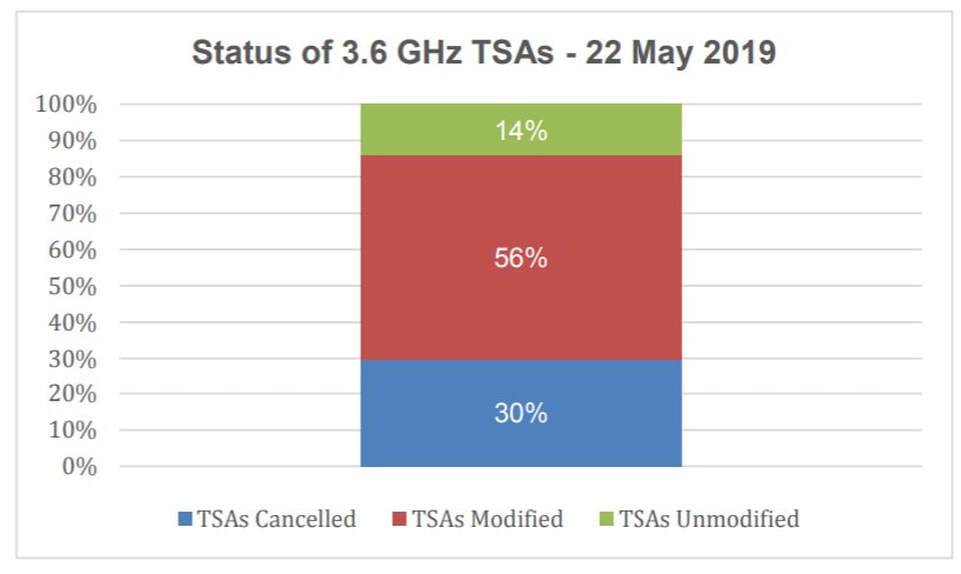
With respect to this, I contacted ComReg seeking clarification on the progress of the migration. The regulator states that 87 Transition Service Areas (just 30% of the total) have been cancelled, 156 (56%) have been modified in frequency or area and 41 (14%) remain unaltered. This data is accurate as of 22 May 2019, and no further changes have been made since that date.
The above represents an unprecedented and ongoing delay, preventing Irish operators from gaining access to large portions of the 3.6GHz band across each region. It is this unwelcome circumstance that has compelled winning bidders to exercise their right to a refund for adjustment of fees, prompting ComReg to give back more than €6 million.
Eir’s non-confidential consultation with ComReg encapsulates the sense of frustration shared by operators.
“With regard to the 3.6GHz band it is correct that ComReg completed an award process however eir is still waiting, one year from licence issue, for access to the spectrum to be commenced. It is a significant failing on the part of ComReg that access to the spectrum has not been forthcoming. This situation cannot persist and ComReg must ensure all transition activity is completed without any further delay.”
With respect to this, I contacted ComReg seeking clarification on the progress of the migration. The regulator states that 87 Transition Service Areas (just 30% of the total) have been cancelled, 156 (56%) have been modified in frequency or area and 41 (14%) remain unaltered. This data is accurate as of 22 May 2019, and no further changes have been made since that date.
The above represents an unprecedented and ongoing delay, preventing Irish operators from gaining access to large portions of the 3.6GHz band across each region. It is this unwelcome circumstance that has compelled winning bidders to exercise their right to a refund for adjustment of fees, prompting ComReg to give back more than €6 million.
Eir’s non-confidential consultation with ComReg encapsulates the sense of frustration shared by operators.
“With regard to the 3.6GHz band it is correct that ComReg completed an award process however eir is still waiting, one year from licence issue, for access to the spectrum to be commenced. It is a significant failing on the part of ComReg that access to the spectrum has not been forthcoming. This situation cannot persist and ComReg must ensure all transition activity is completed without any further delay.”
As a consequence of the transition delays, eir can only fully exploit the 3.6GHz band (80MHz) within the Borders, Midlands and West, and East region. Additionally, most lots within the South West region have been liberalised, along with several lots across other regions. It should be noted that eir forked out more on a per-subscriber basis (€15+) for rights of use in the 3.6GHz band than both of its competitors (€9+).
Out of the operators that purchased spectrum in the 3.6GHz band, Vodafone is bearing the brunt of the impact, with its liberalised use license limited to the Dublin (105MHz) and South East (85MHz) region. This prohibits Big Red from proceeding with a national 5G rollout until spectrum blocks in other regions are vacated by the incumbent users.
The situation is less bleak for Three, with its portion of the 3.6GHz band fully vacated across multiple regions including the South West, South, Dublin, Cork and Galway. A large number of lots have been liberalised in every other region also. From a testing and launch perspective, this puts Three in the best position to utilise its 100MHz of spectrum within the band for a large and diverse geographic 5G launch.
Perhaps the most exasperating aspect of the transition delays isn’t the delays themselves, but how the delays have been communicated. The concealed approach pursued by ComReg during this process is, quite frankly, disturbing. I don’t intend to convey my words lightly, after all, this is an issue of national importance.
Out of the operators that purchased spectrum in the 3.6GHz band, Vodafone is bearing the brunt of the impact, with its liberalised use license limited to the Dublin (105MHz) and South East (85MHz) region. This prohibits Big Red from proceeding with a national 5G rollout until spectrum blocks in other regions are vacated by the incumbent users.
The situation is less bleak for Three, with its portion of the 3.6GHz band fully vacated across multiple regions including the South West, South, Dublin, Cork and Galway. A large number of lots have been liberalised in every other region also. From a testing and launch perspective, this puts Three in the best position to utilise its 100MHz of spectrum within the band for a large and diverse geographic 5G launch.
Perhaps the most exasperating aspect of the transition delays isn’t the delays themselves, but how the delays have been communicated. The concealed approach pursued by ComReg during this process is, quite frankly, disturbing. I don’t intend to convey my words lightly, after all, this is an issue of national importance.
With a chronic lack of spectrum, ComReg has failed Irish consumers.
Another issue of national importance is the crippling lack of spectrum, particularly in high-bands. As Vodafone has articulated on a number of occasions, Ireland lags virtually every other country in Europe for the quantity of spectrum assigned to mobile services.
Just think about that for a second; something has gone wrong somewhere and swift action is required to minimise consumer harm.
Just think about that for a second; something has gone wrong somewhere and swift action is required to minimise consumer harm.
Ireland is one in a list of very few countries in which mobile operators have had to deploy 4G networks with just two spectrum bands at their disposal. And while the true impact of this may be difficult to quantify, a lack of spectrum produces two major drawbacks for consumers: increased cost and poorer network importance.
As a voice in the Irish telecoms industry, I feel it is necessary to join the dots between the above downfalls and a lack of spectrum. On the point of increased costs, much of the rationale stems from the fact that increasing the density of the site grid is incredibly expensive, and this is further exacerbated by Ireland’s topography and population distribution.
However, such densification is required to meet skyrocketing traffic demand when there is an inability to deploy more spectrum with multi-band macrosites. Of course, in a market of Ireland’s size, it is not commercially viable to densify networks to a level that would provide similar performance as simply deploying more spectrum, leading to inferior network performance.
From the above, one would question why Ireland is an outlier in Europe and, more importantly, why ComReg has not made it an absolute priority to release more spectrum for mobile services on this island. To that, I don’t have an answer, and publicly, the regulator doesn’t either.
As a voice in the Irish telecoms industry, I feel it is necessary to join the dots between the above downfalls and a lack of spectrum. On the point of increased costs, much of the rationale stems from the fact that increasing the density of the site grid is incredibly expensive, and this is further exacerbated by Ireland’s topography and population distribution.
However, such densification is required to meet skyrocketing traffic demand when there is an inability to deploy more spectrum with multi-band macrosites. Of course, in a market of Ireland’s size, it is not commercially viable to densify networks to a level that would provide similar performance as simply deploying more spectrum, leading to inferior network performance.
From the above, one would question why Ireland is an outlier in Europe and, more importantly, why ComReg has not made it an absolute priority to release more spectrum for mobile services on this island. To that, I don’t have an answer, and publicly, the regulator doesn’t either.
For example, the 2600MHz (or 2.6GHz) band has been lying fallow here since 2016, when multichannel multipoint distribution system (MMDS) licences expired. That’s an incredible amount of time to leave valuable, high-band spectrum unassigned, and it represents an inefficient use of spectrum.
Across Europe and the wider world, mobile operators have deployed the 2600MHz band where it is required most - dense, urban environments stricken by ever-worsening congestion. There is a mature device ecosystem to support adoption of the band too, with virtually every modern smartphone boasting support.
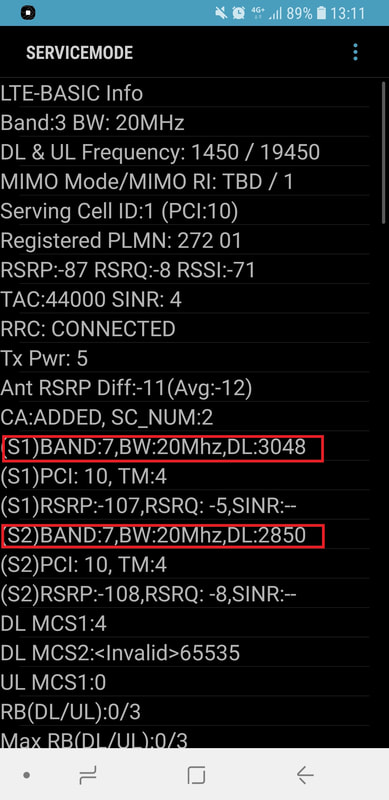
Let’s not forget the most important piece of the pie, Irish operators are desperate to access the 2600MHz band. Heck, I’ve even come across Vodafone testing it in the field, as depicted below. The same operator has also advised ComReg to “accelerate the auctioning of 2.6GHz spectrum” since 2014.
Across Europe and the wider world, mobile operators have deployed the 2600MHz band where it is required most - dense, urban environments stricken by ever-worsening congestion. There is a mature device ecosystem to support adoption of the band too, with virtually every modern smartphone boasting support.
Let’s not forget the most important piece of the pie, Irish operators are desperate to access the 2600MHz band. Heck, I’ve even come across Vodafone testing it in the field, as depicted below. The same operator has also advised ComReg to “accelerate the auctioning of 2.6GHz spectrum” since 2014.
From one angle, it would appear the reason why the 2600MHz band is still awaiting assignment is that ComReg decided to fast track liberalisation of the 3.6GHz band instead. As detailed earlier, that strategy isn’t going so well.
An ambitious multi-band award is to Ireland what water is to a desiccated flower.
To the relief of all the mentioned concerns about the chronic lack of spectrum in the Irish mobile market, ComReg has, finally, proposed a solution - a multi-band award in which 350MHz of spectrum, both low and high-band, will be released for mobile services. This is a momentous breakthrough and a turning point for Ireland’s telecoms industry.
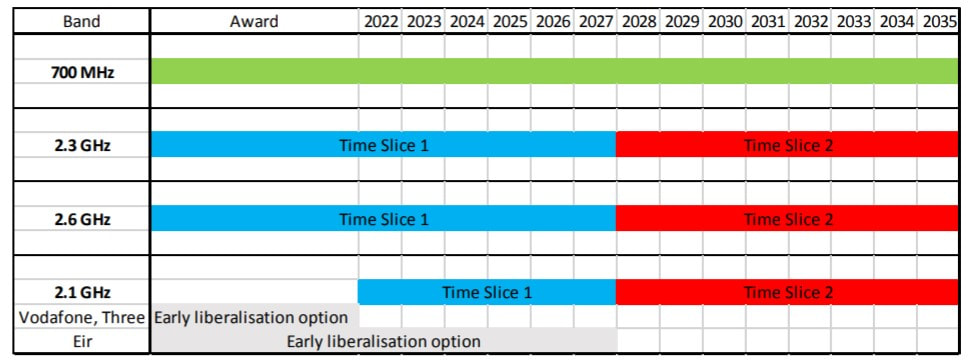
In the proposed spectrum award, ComReg intends to release the 700MHz, 2300MHz and 2600MHz bands. When made available, these bands, which are harmonised across the European Union, will increase the total amount of spectrum allocated for mobile services on this island by a wapping 42%.
In the proposed spectrum award, ComReg intends to release the 700MHz, 2300MHz and 2600MHz bands. When made available, these bands, which are harmonised across the European Union, will increase the total amount of spectrum allocated for mobile services on this island by a wapping 42%.
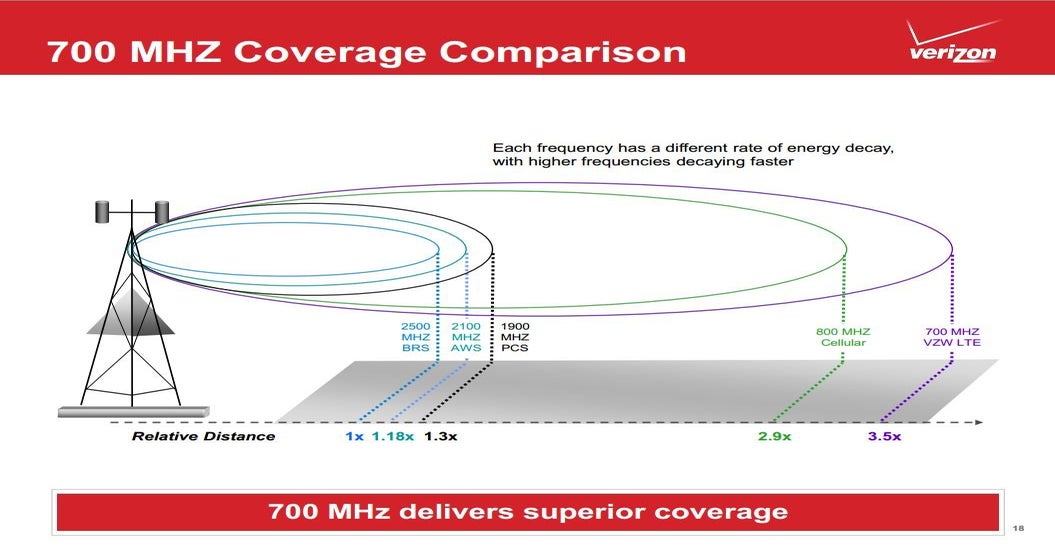
If we have aspirations to connect the disconnected, the 700MHz band will be pivotal.
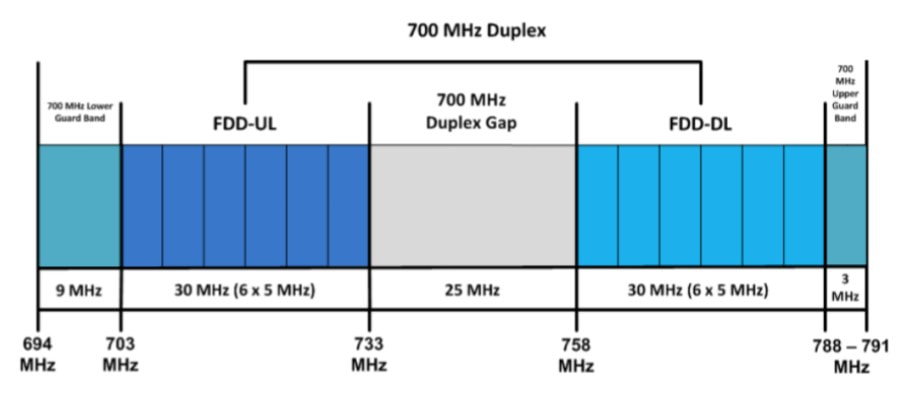
For rural dwellers, and even for those that spend a large amount of time in cement-laden, energy-efficient buildings, liberalisation of the 700MHz band (703-733 / 758-788MHz) should be of particular interest. As low-band spectrum, it exhibits excellent propagation characteristics, allowing each radio site to provide an expansive geographic coverage footprint.
This is why it is being pursued as a pioneer band for 5G deployments that focus on coverage, cost-effectively extending the reach of next-generation networks into rural communities. These coverage enhancements will be profound; ComReg estimates that when used in conjunction with existing low-band assets, the 700 MHz Duplex (2x10MHz) will provide a 65% coverage area gain for speeds of 30Mbps.
This is why it is being pursued as a pioneer band for 5G deployments that focus on coverage, cost-effectively extending the reach of next-generation networks into rural communities. These coverage enhancements will be profound; ComReg estimates that when used in conjunction with existing low-band assets, the 700 MHz Duplex (2x10MHz) will provide a 65% coverage area gain for speeds of 30Mbps.
Moreover, liberalisation of the 700MHz band also provides mobile operators with the liberty to enhance network capacity, a feat that can be achieved by aggregating more carriers. Given the fact that enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) is a core feature of 5G NR, and one which is likely to enjoy healthy adoption in rural Ireland, utilisation of 700MHz as an aggregation band is forthcoming.
Historically, RTÉ has been an incumbent occupier of the 700MHz band, using the spectrum to support its Digital Terrestrial Television (DTT) transmission network. 2RN (which operates RTÉ’s infrastructure) is in the process of vacating the spectrum, with DTT licenses scheduled to expire before 4 March 2020.
Within the band, there is 96MHz of contiguous spectrum available. However, ComReg only intends to release 2x30 MHz of spectrum in the 700 MHz Duplex, which is composed of 703-733 MHz (FDD uplink) paired with 758- 788 MHz (FDD downlink). The 700MHz Duplex Gap and Guard Bands will remain fallow because the device ecosystem has not matured to support the use of the spectrum yet.
Interestingly, ComReg intends to use the 700MHz award as an opportunity to introduce more stringent coverage obligations, something that Irish operators have skillfully evaded up until now. In an unrelenting quest to end the digital divide on this island, it is only fitting that concrete actions are put in place to incentivise investment in peripheral regions.
Historically, RTÉ has been an incumbent occupier of the 700MHz band, using the spectrum to support its Digital Terrestrial Television (DTT) transmission network. 2RN (which operates RTÉ’s infrastructure) is in the process of vacating the spectrum, with DTT licenses scheduled to expire before 4 March 2020.
Within the band, there is 96MHz of contiguous spectrum available. However, ComReg only intends to release 2x30 MHz of spectrum in the 700 MHz Duplex, which is composed of 703-733 MHz (FDD uplink) paired with 758- 788 MHz (FDD downlink). The 700MHz Duplex Gap and Guard Bands will remain fallow because the device ecosystem has not matured to support the use of the spectrum yet.
Interestingly, ComReg intends to use the 700MHz award as an opportunity to introduce more stringent coverage obligations, something that Irish operators have skillfully evaded up until now. In an unrelenting quest to end the digital divide on this island, it is only fitting that concrete actions are put in place to incentivise investment in peripheral regions.
That said, I think we should approach the topic of coverage obligations with great caution. In cases where obligations are excessively demanding, there are negative impacts for consumers and market competition, spawning from an artificial constriction of commercial choices at the disposal of operators.
For its part, ComReg is proposing to define coverage obligations that are “precautionary in nature, and are towards the upper end of the range of commercially realistic competitive outcomes”. Such a strategy is likely to ruffle some feathers within the industry and believe me, it already has.
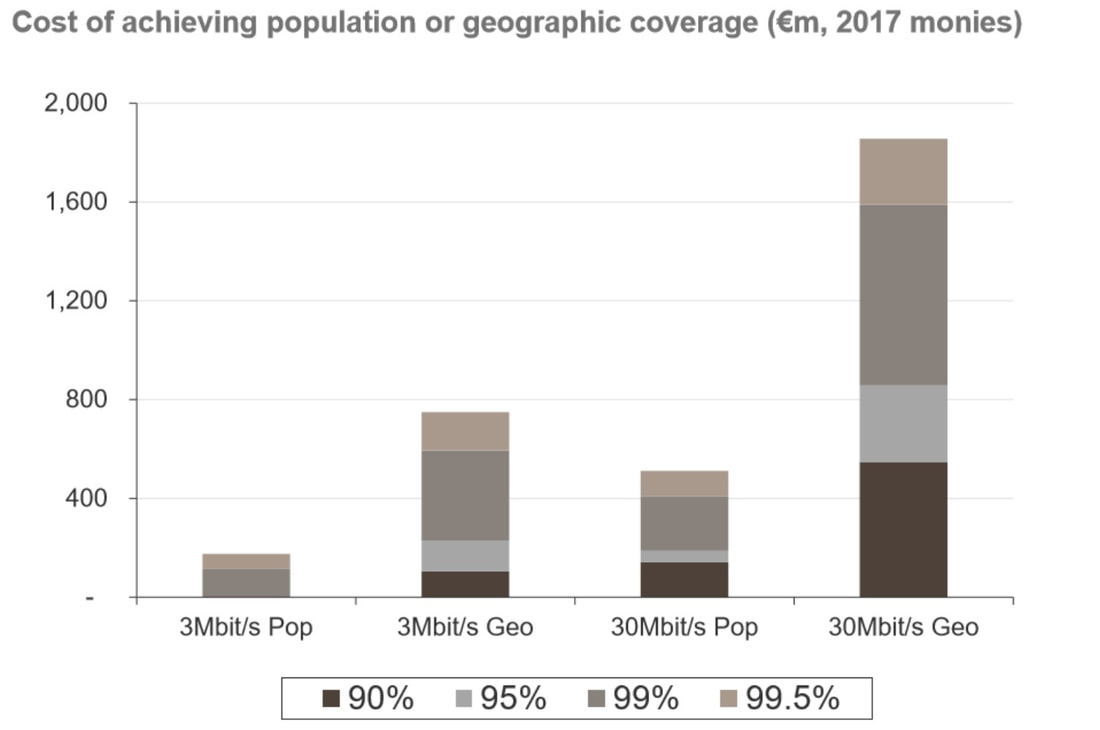
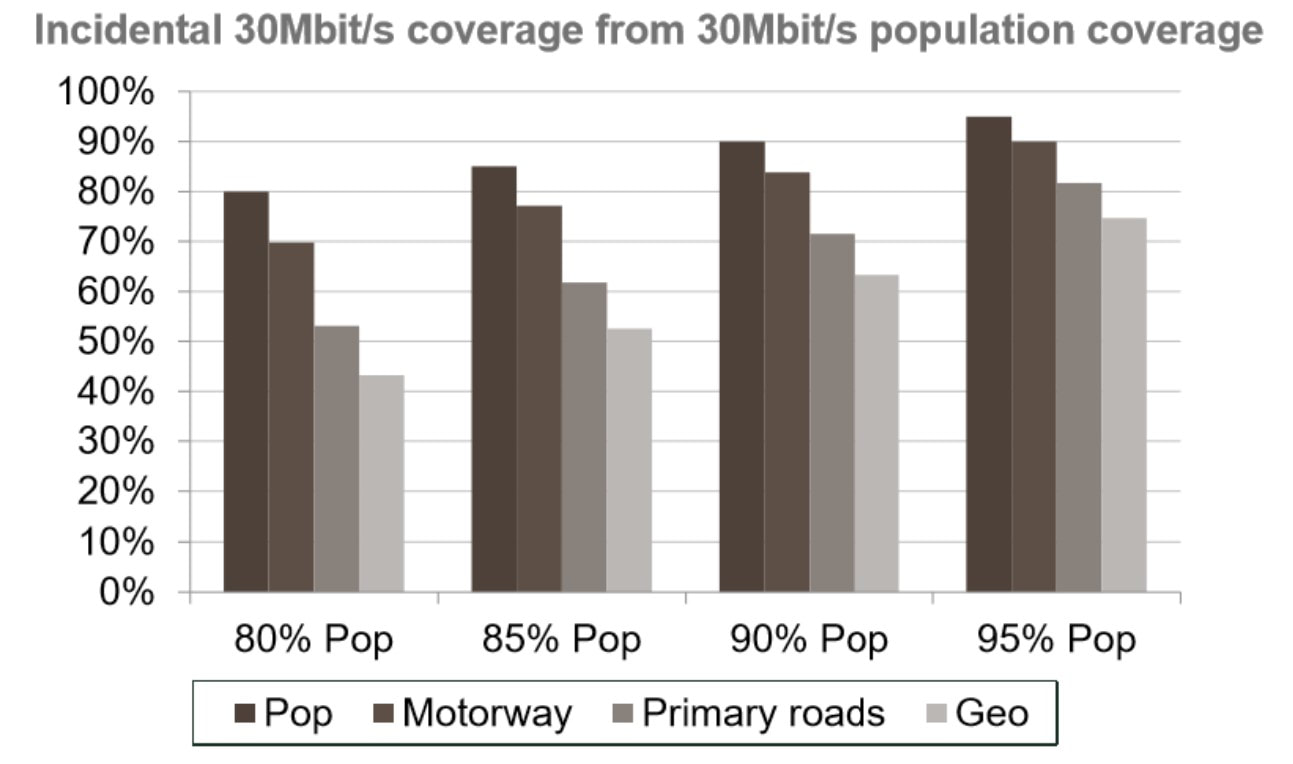
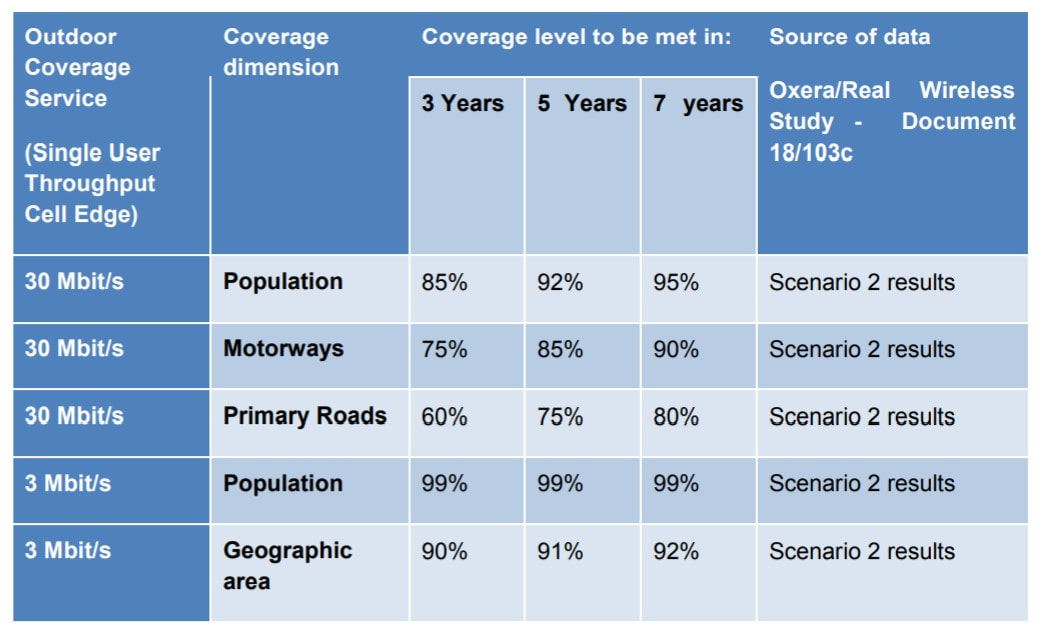
On a more technical level, the proposed coverage obligations would require 700MHz license holders to provide a 3Mbps service (at the cell edge) to 99% of the Irish population and to 92% of the geographic area of Ireland. At a higher level, there is an obligation to provide a 30Mbps service to 95% of the population, 90% of motorways, and 80% of primary roads.
For its part, ComReg is proposing to define coverage obligations that are “precautionary in nature, and are towards the upper end of the range of commercially realistic competitive outcomes”. Such a strategy is likely to ruffle some feathers within the industry and believe me, it already has.
On a more technical level, the proposed coverage obligations would require 700MHz license holders to provide a 3Mbps service (at the cell edge) to 99% of the Irish population and to 92% of the geographic area of Ireland. At a higher level, there is an obligation to provide a 30Mbps service to 95% of the population, 90% of motorways, and 80% of primary roads.
Notably, the incidental geographic coverage of providing a 30Mbps service to 95% of the population is in the region of 75%, relatively close to the level of 4G availability today. In addition to the above obligations, ComReg has also outlined a requirement to provide voice calls and a 30Mbps service to 345 specific locations, all of which have been defined by a Focus Group within the Mobile Phone and Broadband Taskforce.
The 345 specific locations consist of “40 business and technology parks (including strategic sites), 65 hospitals, 24 higher education campuses, 14 air and seaports, 160 train and bus stations, and 42 top visitor attraction information points.”
As a capacity layer, the 2300MHz band will be important for both mobile and FWA.
Set to join the liberalisation of the 700MHz band is 2300MHz (2300 – 2400MHz), a contiguous 100MHz block which will play an integral role in enhancing the capacity of both mobile and fixed wireless networks in Ireland.
Again, there is a mature device ecosystem to support the use of this band, and it is widely available in other markets such as the UK and Asia. From a propagation perspective, it mirrors quite closely the characteristics of the existing 2100MHz (3G) and 2600MHz bands.
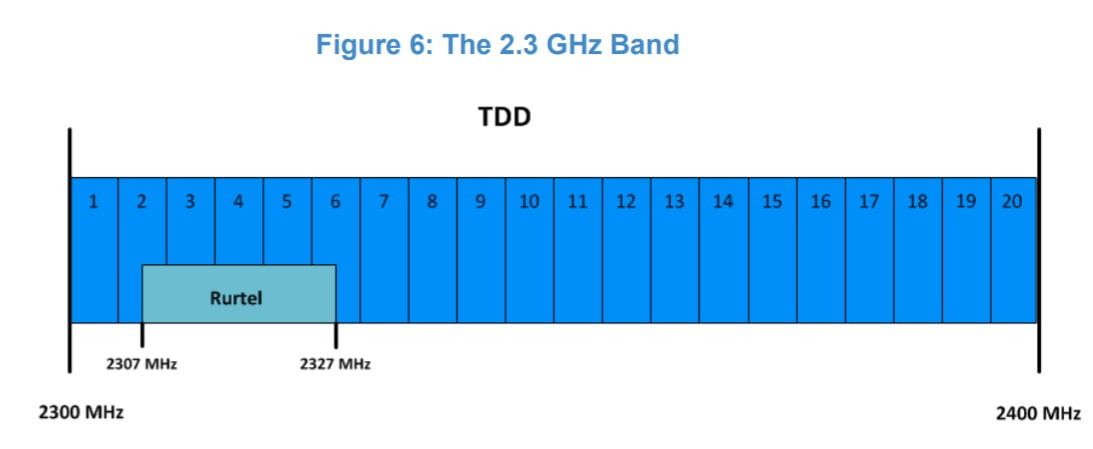
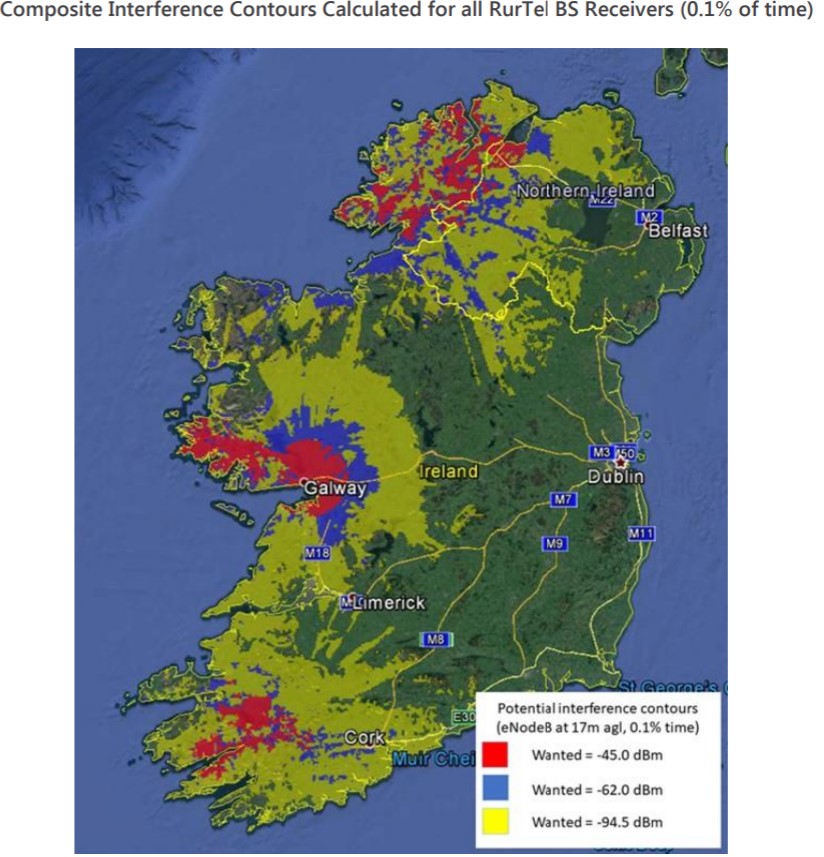
The band is unused in the vast majority of Ireland, and that also applies to urban areas, where its availability is most important. In rural parts of Kerry, Galway and Donegal, eir maintains a license to operate its RurTel service within the band (47 sites). RurTel, if you’ve never heard of it, is a point-to-multipoint system offering fixed telephony, essentially allowing eir to meet its universal service obligation (USO).
The band is unused in the vast majority of Ireland, and that also applies to urban areas, where its availability is most important. In rural parts of Kerry, Galway and Donegal, eir maintains a license to operate its RurTel service within the band (47 sites). RurTel, if you’ve never heard of it, is a point-to-multipoint system offering fixed telephony, essentially allowing eir to meet its universal service obligation (USO).
ComReg has hinted that the number of RurTel subscribers is very low and declining, but for some poor souls, it is the only fixed telephony service in operation at their address. Because of the latter, the regulator is proposing to release national licenses for the band with “possibly a limited number of temporary coordination zones corresponding to the areas and frequencies covered by Eir’s existing Rurtel licences”.
We should note, however, that the perceived criticality of the 2300MHz band is lesser than that of the 700MHz and 2600MHz bands.
We should note, however, that the perceived criticality of the 2300MHz band is lesser than that of the 700MHz and 2600MHz bands.
The days of the 2600MHz band lying fallow are becoming limited.
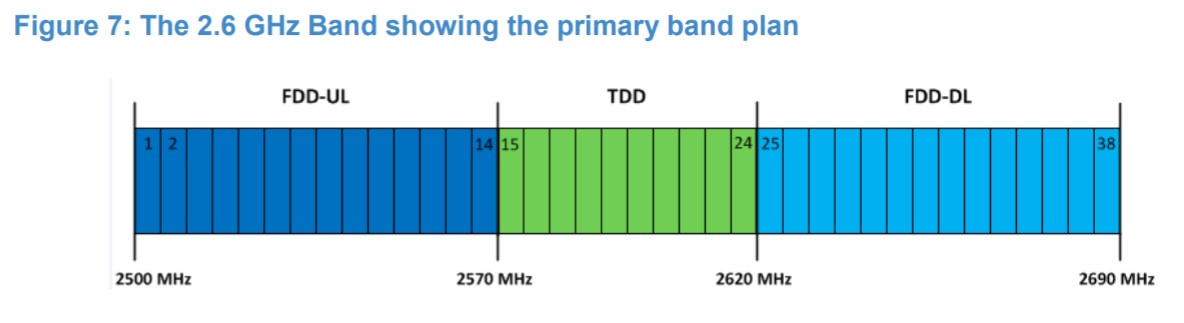
We’ve already mulled the 2600MHz band (2500 – 2690 MHz) and the ludicrous fact that it has been left untouched and unused since 2016. Gladly, ComReg is proposing an overdue remedy to that by committing to releasing 190MHz of spectrum within the band. You know what they say, better late than never.
The band can be broken into two distinct parts, namely the 2600MHz Duplex and Duplex Gap. For the former, due to FDD operation, it is broken into 2500–2570 MHz (uplink) paired with 2620–2690 MHz (downlink). In short, this means the Duplex Gap offers 2x70MHz FDD.
In the middle presides the 2600MHz Duplex (2570 – 2620 MHz), a contiguous 50 MHz block. As with the bands mentioned prior to this, ComReg intends to make them available for an overall period of fifteen years.
The band can be broken into two distinct parts, namely the 2600MHz Duplex and Duplex Gap. For the former, due to FDD operation, it is broken into 2500–2570 MHz (uplink) paired with 2620–2690 MHz (downlink). In short, this means the Duplex Gap offers 2x70MHz FDD.
In the middle presides the 2600MHz Duplex (2570 – 2620 MHz), a contiguous 50 MHz block. As with the bands mentioned prior to this, ComReg intends to make them available for an overall period of fifteen years.
Rife with complexity, the 2100MHz band resurfaces concerns about spectrum asymmetry.
Up until this point, I’ve purposely neglected to mention the planned liberalisation of the 2100MHz band, and for one clear reason: it’s a minefield. At present, each operator holds a license to provide 3G (UMTS) services within the band. Therein lies the problem, the current 2100MHz licenses are not technology-agnostic, preventing deployment of 4G and 5G services in the band.
This is a big problem. Not only has it artificially limited the performance capabilities of Ireland’s 4G networks, but it is also forcing operators to prepare for the continued existence of 3G networks on this island. In an idyllic Ireland, the 3G switch off will occur before 2025, leaving 2G as the remaining base and legacy network.
But, liberalising the paired 2100MHz band won’t be a walk in the park as there are many inherent complexities. This is why operators are urging ComReg to defer the re-awarding of the band until after the detailed multi-band spectrum award has taken place.
This is a big problem. Not only has it artificially limited the performance capabilities of Ireland’s 4G networks, but it is also forcing operators to prepare for the continued existence of 3G networks on this island. In an idyllic Ireland, the 3G switch off will occur before 2025, leaving 2G as the remaining base and legacy network.
But, liberalising the paired 2100MHz band won’t be a walk in the park as there are many inherent complexities. This is why operators are urging ComReg to defer the re-awarding of the band until after the detailed multi-band spectrum award has taken place.
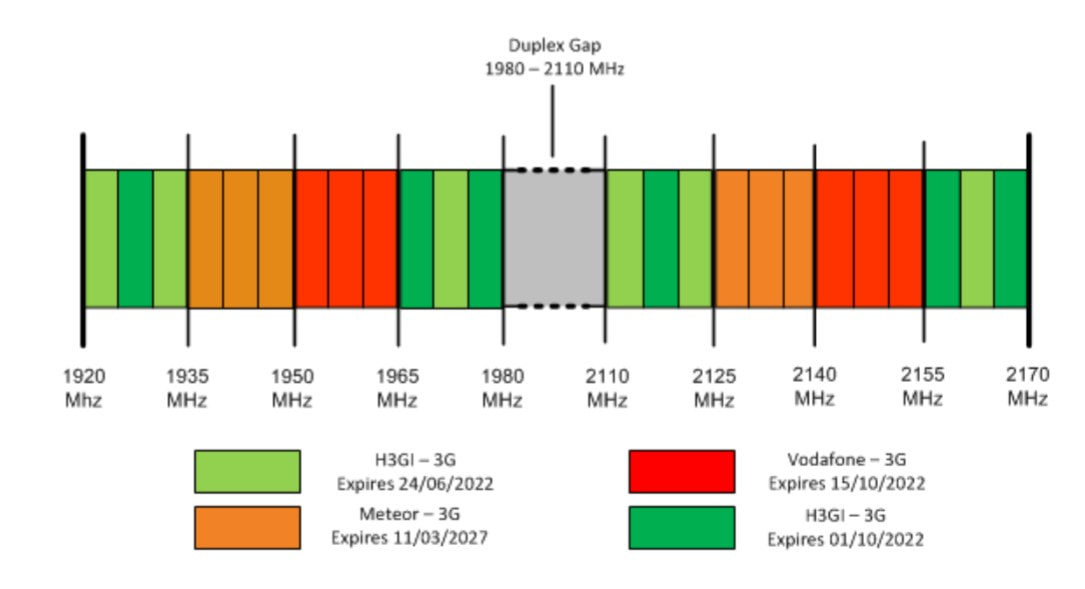
The primary complexity that is overshadowing liberalisation efforts is the wildly divergent expiration dates for existing licenses. Keeping the merger in mind, Three boasts the largest amount of spectrum in the 2100MHz band, with two licences covering 2x30MHz. Both Vodafone and eir hold a license covering 2x15MHz.
While Vodafone and Three’s licenses will expire between June and October in 2022, for eir, expiration is not scheduled until Match 2027. As mentioned, each operator will inevitably decommission their 3G network within the coming decade, perhaps reverting to their 900MHz assets soon, but without early liberalisation, eir will be at a colossal disadvantage.
Early liberalisation of the band confronts eir “with the prospect of effectively paying for licence renewal a number of years in advance of licence expiry”. ComReg is proposing to tackle this issue by awarding new rights in time slices, a similar approach pursued in the 2012 multi-band award for 900MHz (GSM).
In ComReg’s proposals, time slice 1 will consist of 90MHz (2×45 MHz), while time slice 2 will consist of 120MHz (2×60 MHz). This approach also requires the alignment of existing 3G licenses to expire 15 October 2022, allowing a uniform commencement date for time slice 1.
While Vodafone and Three’s licenses will expire between June and October in 2022, for eir, expiration is not scheduled until Match 2027. As mentioned, each operator will inevitably decommission their 3G network within the coming decade, perhaps reverting to their 900MHz assets soon, but without early liberalisation, eir will be at a colossal disadvantage.
Early liberalisation of the band confronts eir “with the prospect of effectively paying for licence renewal a number of years in advance of licence expiry”. ComReg is proposing to tackle this issue by awarding new rights in time slices, a similar approach pursued in the 2012 multi-band award for 900MHz (GSM).
In ComReg’s proposals, time slice 1 will consist of 90MHz (2×45 MHz), while time slice 2 will consist of 120MHz (2×60 MHz). This approach also requires the alignment of existing 3G licenses to expire 15 October 2022, allowing a uniform commencement date for time slice 1.
But, the complexity doesn’t just constitute different license expiry dates, it also includes the very real and negative competitive implications of proceeding with liberalisation in its current state. Yes, I am referring to the stark spectrum disparity between Irish operators, something that would be exacerbated if Three manages to maintain its current 2100MHz portfolio post-liberalisation.
For context on the imbalance, Three holds 50% of the 2100MHz band, 47% of the 1800MHz band and 43% of the 900MHz band. As eir describes, “If left unaddressed, this spectrum imbalance significantly distorts the competitive landscape” in Ireland. And, unequivocally, I agree with that stance.
It is so critical that ComReg approaches liberalisation of the 2100MHz band with an intent to prevent the distortion of competition, not just in the immediate future but in the longer-term, by pushing for the equalisation of spectrum holdings in the band.
For context on the imbalance, Three holds 50% of the 2100MHz band, 47% of the 1800MHz band and 43% of the 900MHz band. As eir describes, “If left unaddressed, this spectrum imbalance significantly distorts the competitive landscape” in Ireland. And, unequivocally, I agree with that stance.
It is so critical that ComReg approaches liberalisation of the 2100MHz band with an intent to prevent the distortion of competition, not just in the immediate future but in the longer-term, by pushing for the equalisation of spectrum holdings in the band.
Conclusion: A Brighter Future Awaits
Ireland has dragged its feet in the 4G race, and while so many different factors have contributed to this, some are more evident than others. In the 2012 multi-band award, spectrum acquisition fees were extraordinarily excessive, inhibiting the ability of operators to deploy wide-area 4G networks. Lo and behold, today, Ireland lags most other developed countries for 4G availability. This trend should not be repeated in the upcoming multi-band award.
The failure to release more spectrum for mobile services has handicapped Irish operators, exposing consumers to the impacts of progressive degradation of network performance, all at a time when data traffic is growing exponentially and average revenue per user (APRU) is declining. This trend of skimping on spectrum releases should not be repeated in the 5G era.
Transition troubles at 3.6GHz are delaying the execution of plans for 5G deployment, but incredulously, it would appear ComReg doesn't view this as a major problem. This trend should not be repeated with the liberalisation of other bands such as 2.3GHz.
By reflecting on these mistakes, we can work to build a brighter future for Ireland, and I think the tide is already turning in that direction as we explore new ways to provide a competent mobile service to more people with more coverage obligations, more spectrum and more collaboration across each layer within this wonderful industry.
The failure to release more spectrum for mobile services has handicapped Irish operators, exposing consumers to the impacts of progressive degradation of network performance, all at a time when data traffic is growing exponentially and average revenue per user (APRU) is declining. This trend of skimping on spectrum releases should not be repeated in the 5G era.
Transition troubles at 3.6GHz are delaying the execution of plans for 5G deployment, but incredulously, it would appear ComReg doesn't view this as a major problem. This trend should not be repeated with the liberalisation of other bands such as 2.3GHz.
By reflecting on these mistakes, we can work to build a brighter future for Ireland, and I think the tide is already turning in that direction as we explore new ways to provide a competent mobile service to more people with more coverage obligations, more spectrum and more collaboration across each layer within this wonderful industry.
Understanding VoLTE: The Voice of TomorrowA generational leap in cellular voice requires a leap of faith.
|